Controller Area Network (ISO 11898)
why do we need CANBus
Cars are prior means of transportation, in older cars they had basic electrical wiring as time went on the demand for more features was increased to gain competitive advantage and also comply with new regulations, As we are literally and figuratively turning the corner into the era of the driver less or autonomous car, hacking automobiles will become even more important and dangerous.
The automobile industry uses many protocols in modernized vehicles with embedded systems and Electronic control units (ECU) which can communicate with each other using protocols like CAN.
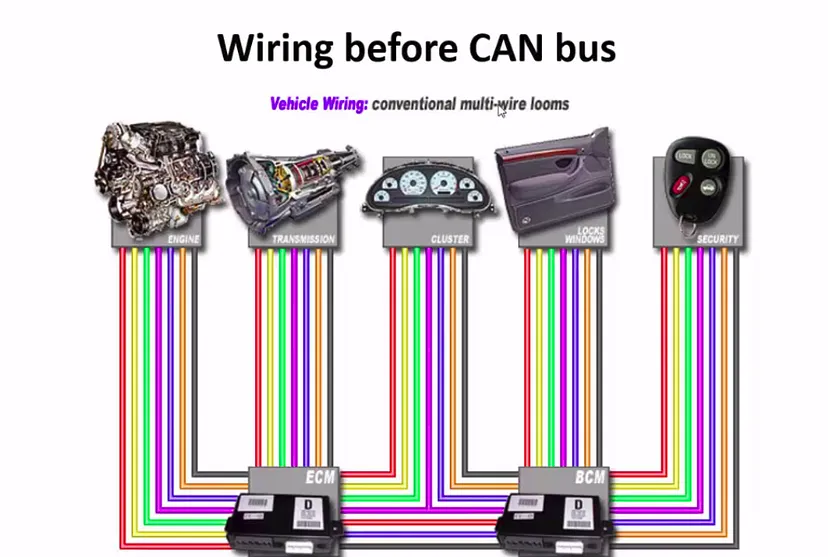
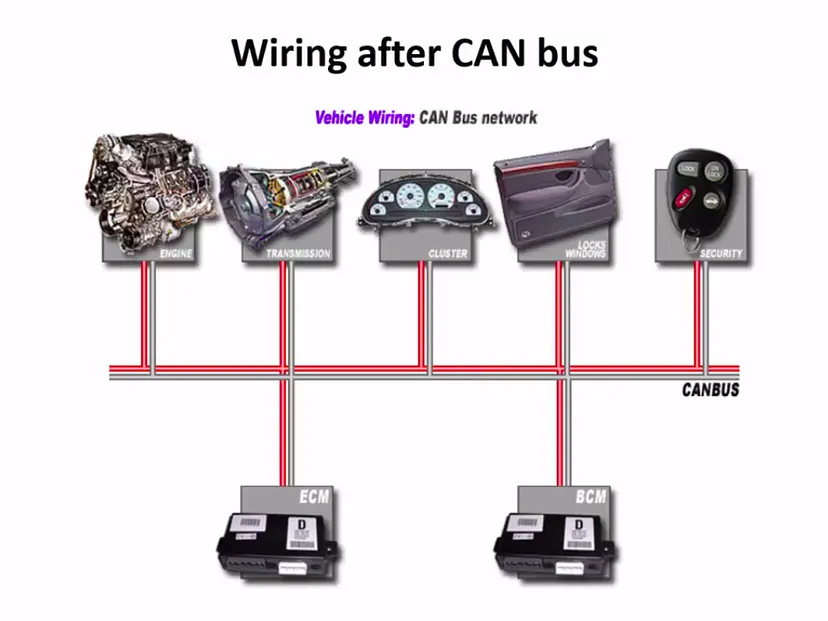
The most widely used protocols in Automobiles is CAN and its flavors, Let’s learn about CAN, it was first developed by Bosch and released in SAE {1986} it was designed for robust communications within the vehicle microcontrollers and devices without the need of a computer.
Protocol Overview
CAN protocol runs over two wires CAN-H and CAN-L, it works on the method of differential signaling it transmits the message by differing the voltage between two wires.
CAN protocol runs over two wires CAN-H and CAN-L, it works on the method of differential signaling “Differential signaling is a method for electrically transmitting information using two complementary signals. The technique sends the same electrical signal as a differential pair of signals, each in its own conductor. The pair of conductors can be wires or traces on a circuit board.” it transmits the data by differing the voltage between two wires. This provides a viable data transmission as it can resist noises and disturbances.
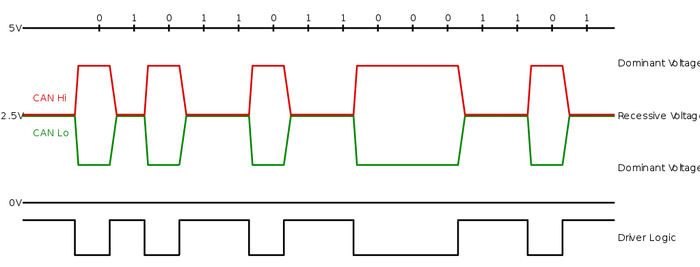
CAN is a multi master serial bus connected with ECU’s{nodes}. all of them are connected to each other through a two wire bus which consists of a 120-ohm resistor at the end of them to terminate the data.
CAN-H will be at 5 v and CAN-L at 0 v and while transmitting a dominant (0) and does not drive either wire when transmitting a recessive (1). Designating “0” as dominant gives the nodes with the lower ID numbers priority on the bus.
The dominant differential voltage is a nominal 2 V. The termination resistor passively returns the two wires to a nominal differential voltage of 0V.
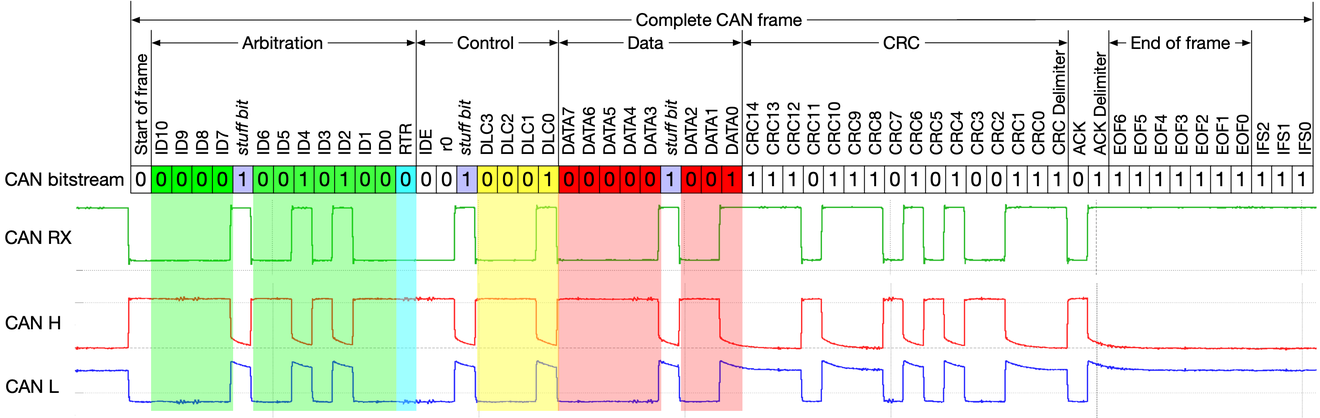
The frame format is as follows: The bit values are described for CAN-LOW signal.
| Field name | Length (bits) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Start-of-frame | 1 | Denotes the start of frame transmission |
| Identifier (green) | 11 | A (unique) identifier which also represents the message priority |
| Stuff bit | 1 | A bit of the opposite polarity to maintain synchronization |
| Remote transmission request (RTR) | 1 | Must be dominant (0) for data frames and recessive (1) for remote request frames |
| Identifier extension bit (IDE) | 1 | Must be dominant (0) for base frame format with 11-bit identifiers |
| Reserved bit (r0) | 1 | Reserved bit. Must be dominant (0), but accepted as either dominant or recessive |
| Data length code (DLC) (yellow) | 4 | Number of bytes of data (0–8 bytes) |
| Data field (red) | 0–64 (0-8 bytes) | Data to be transmitted (length in bytes dictated by DLC field) |
| CRC | 15 | Cyclic redundancy check |
| CRC delimiter | 1 | Must be recessive (1) |
| ACK slot | 1 | Transmitter sends recessive (1) and any receiver can assert a dominant (0) |
| ACK delimiter | 1 | Must be recessive (1) |
| End of frame (EOF) | 7 | Must be recessive (1) |
| Inter frame spacing (IFS) | 3 | Must be recessive (1) |
- Data frame: a frame containing node data for transmission.
- Remote frame: a frame requesting the transmission of a specific identifier.
- Error frame: a frame transmitted by any node detecting an error.
- Overload frame: a frame to inject a delay between data or remote frame.
- Arbitration ID: This is different for different nodes and acts as a unique identifier to each node.
- Data Length Code: Represents the bytes of data in the message.
- Data: The data sent or received.
- SOF and EOF: Used to separate messages.
The data is autonomous in the CAN network and if a receiver node wants to request certain data from a sender the remote frame is used. if an error is detected from the network by a node it reacts with,
Six dominant bits — error active, Six recessive bits — error passive.
There are two types of CAN packets: standard and extended.
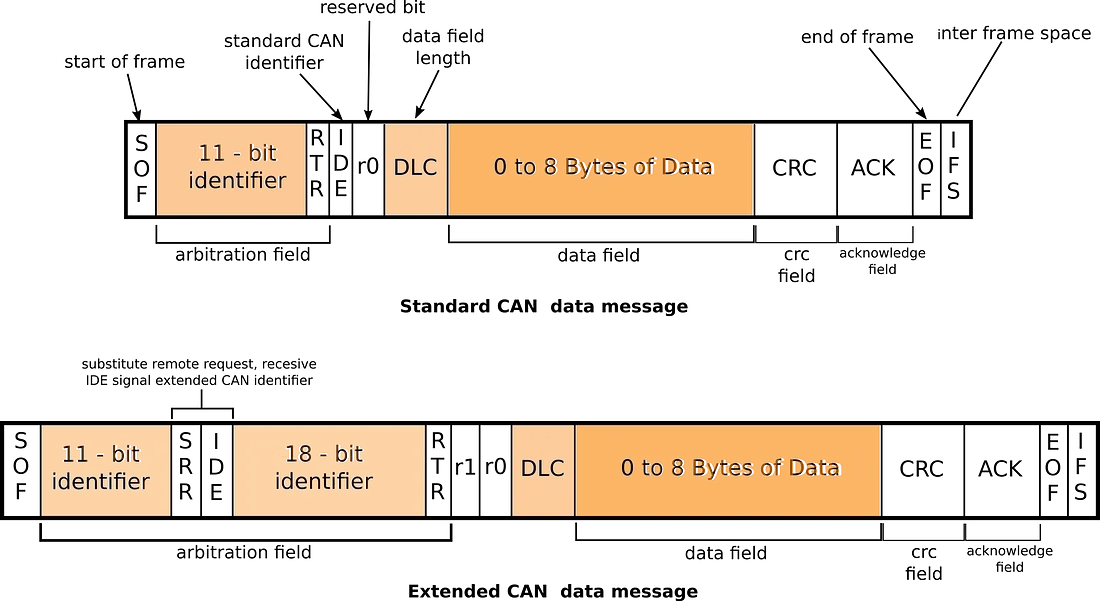
The frame format is as follows on from here in the table below:
| Field name | Length (bits) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Start-of-frame | 1 | Denotes the start of frame transmission |
| Identifier A (green) | 11 | First part of the (unique) identifier which also represents the message priority |
| Substitute remote request (SRR) | 1 | Must be recessive (1) |
| Identifier extension bit (IDE) | 1 | Must be recessive (1) for extended frame format with 29-bit identifiers |
| Identifier B (green) | 18 | Second part of the (unique) identifier which also represents the message priority |
| Remote transmission request (RTR) (blue) | 1 | Must be dominant (0) for data frames and recessive (1) for remote request frames |
| Reserved bits (r1, r0) | 2 | Reserved bits which must be set dominant (0), but accepted as either dominant or recessive |
| Data length code (DLC) (yellow) | 4 | Number of bytes of data (0–8 bytes) |
| Data field (red) | 0–64 (0-8 bytes) | Data to be transmitted (length dictated by DLC field) |
| CRC | 15 | Cyclic redundancy check |
| CRC delimiter | 1 | Must be recessive (1) |
| ACK slot | 1 | Transmitter sends recessive (1) and any receiver can assert a dominant (0) |
| ACK delimiter | 1 | Must be recessive (1) |
| End-of-frame (EOF) | 7 | Must be recessive (1) |
| Inter-frame spacing (IFS) | 3 | Must be recessive (1) |
The two identifier fields (A & B) combine to form a 29-bit identifier.
Extended packets are like standard ones but with a larger space to hold IDs.extended packets use substitute remote request SRR instead of RTR with SSR set to 1. They’ll also have the IDE set to 1, and their packets will have an 18-bit identifier.
CAN protocol reduces wiring and provides the ability to work in different electrical environments and ensures noise free transmission. Traffic congestion is eliminated as the messages are transmitted based on their priority and it allows the entire network to meet the timing constraints. It provides for error free transmission as each node can check for errors during the transmission of the message and send the error frame. But, CAN is like a basic flavor of protocols. many other protocols are developed by highlighting specific capabilities of CAN.
Arbitration in CANBus
For a highly populated network, the performance depends upon the data transmission. in a CAN network, the data each node sends and receives moves it all. it is like the network should be shared efficiently among all its constituents.
we should remember that it is not like any Master-slave communication, literally any node and all nodes will send and receives the data according to its function which of course the priority of transmission depends on the situation. the goal of the network arbitration here is to push and pull data reliably by every node.
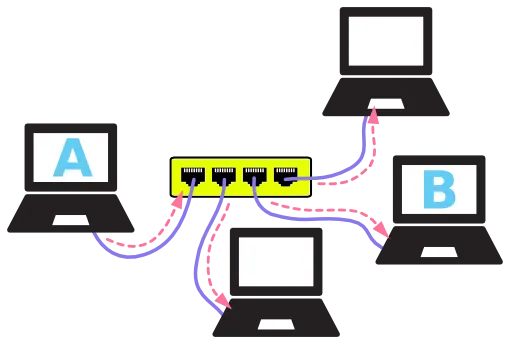
For example in a computer network connected with Ethernet the {CSMA/CD} carrier sense, multiple access with collision detection will be In charge if there is a collision it stops the transmission of data and starts again after some time.
The CAN bus network arbitration is more like an updated version of Ethernet’s network arbitration. Non Destructive collision detection makes it easier. In the case of two messages are pushed into the network at the same time one with the least arbitration ID will win over the other one and continues to transmit, now another one will wait for some time and starts transmitting again.
the least arbitration ID denotes the message’s priority which is decided by the designer at the time of Designing the network, Message priority is very important in the case of an autonomous car, like the intrusion detection message should reach the breaking system ASAP within milliseconds.
CAN bus also has two different types of network’s High speed CAN bus which supports bitrates up to 1 Mbits/sec, it is a most commonly used one also a base for protocols like CAN FD, CANopen & SAE J1939. Low speed CAN bus (or ISO 11898-3) is a fault tolerant version as it can continue communication regardless of failure in one wire.
CAN bus network is also a completely centralised network, this makes it flexible to add new nodes and run diagnostics from one point of the network. The fully centralized network with efficiency and robustness in transmitting essential data makes it practical to be used in vehicles and industrial machinery widely across different industries like Heavy duty fleet telematics, Airplanes, manufacturing plants and medical equipment.
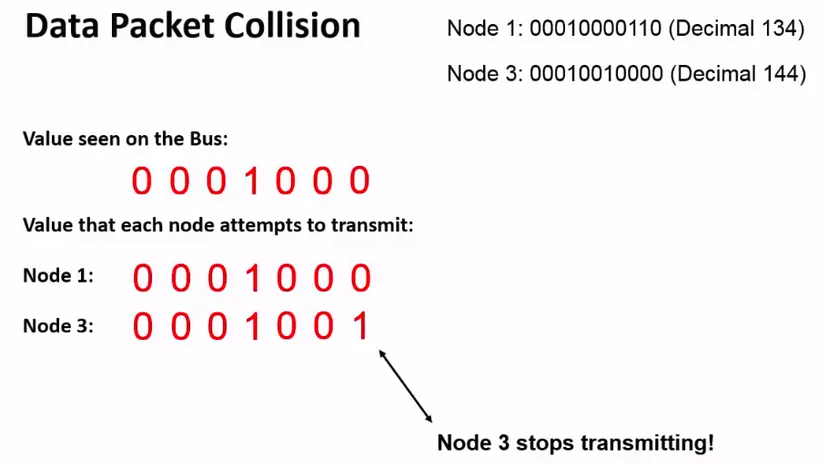
Here, two nodes will start pushing the messages without acknowledging other nodes activity meanwhile it also reads the data from the bus, in the above case both nodes 1 &3 pushes their arbitration id’s and in the meantime when node 3 sends a recessive bit (1) and observes dominant bit (0) it will stop transmitting messages and waits for some time and starts again. there will be different clock speeds for each node to avoid the mess in the network.
Is CAN Bus Outdated?
One of the best alternatives to CAN bus is Ethernet TCP/IP. it also cannot provide reliability, excellent error detection and fault confinement capabilities like CAN bus.
We are already into data era and the maximum of 8 bytes data transmitting capability of CAN need a revamp. So, engineers came up with multiple protocols which are developed upon CAN bus specific to a particular network architecture type. Like, CANopen for Industrial robotics, CAN FD for higher data rates (up to 8 Mbits/sec), payload size up to 64 bytes and improved security via authentication.
Conclusion
The top benefits of using CAN Bus protocol are Low cost implementation, completely centralized network, Extreme robust and efficient.On the other hand, it also comes short if we are looking more for security as CAN bus is not secure by design.
So, Automotive manufacturers are adding different network busses like LIN bus and CAN FD buses to improve the vehicle architecture more. But, ISO 11898 is not going to fade away any soon.
References
I hope this blog post gave you a good high level overview of CAN Bus protocol. If you are reading up to this point, you might be interested in Automotive security. This blog post aimed to give you an idea about CAN Bus protocol which is widely used in Automotive architecture. Going forward, i will try to add more intresting blogs like this one so, keep an eye on this blog page. I hope you enjoyed reading this as much as I enjoyed writing it :) made with <3 Kartheek Lade